Gestational diabetes log sheets are essential tools for monitoring blood sugar levels, helping women manage their condition effectively during pregnancy․ They enable tracking of fasting and postprandial glucose levels, insulin doses, and daily activities, providing valuable insights for healthcare providers to optimize treatment plans and improve health outcomes․
1․1 What is Gestational Diabetes?
Gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) is a condition where women without a prior diabetes diagnosis develop high blood glucose levels during pregnancy․ It typically occurs in the second or third trimester and often resolves after pregnancy․ However, it increases risks for both mother and baby, such as complications during delivery or preterm birth․ Managing gestational diabetes is crucial to ensure a healthy pregnancy outcome and reduce long-term health risks․
1․2 Importance of Tracking Blood Sugar Levels
Tracking blood sugar levels is vital for managing gestational diabetes, ensuring both mother and baby’s health․ Regular monitoring helps maintain glucose within target ranges, preventing complications like preterm labor or macrosomia․ By recording fasting and postprandial levels, individuals can identify patterns, adjust diets, and make informed decisions; Consistent tracking also aids healthcare providers in tailoring treatment plans, promoting a safer pregnancy and reducing long-term health risks for the mother and child․

Components of a Gestational Diabetes Log Sheet
A gestational diabetes log sheet includes blood glucose levels, monitoring times, insulin doses, meals, and notes․ It helps track patterns, guide decisions, and ensure healthy outcomes․
2․1 Blood Glucose Monitoring Times
Blood glucose monitoring typically occurs four times daily: fasting (upon waking), after breakfast, after lunch, and after dinner․ Consistent tracking helps identify patterns and ensures levels stay within target ranges, crucial for managing gestational diabetes effectively․ Regular monitoring, especially at these specific times, provides valuable data for adjusting meals, exercise, and medication, helping maintain maternal and fetal health throughout pregnancy․
2․2 Recording Fasting and Postprandial Levels
Accurate recording of fasting and postprandial blood glucose levels is vital for managing gestational diabetes․ Fasting levels are measured upon waking, typically before eating, while postprandial levels are recorded 1-2 hours after meals․ Keeping track of these readings helps identify patterns and ensures blood sugar stays within target ranges, usually below 95 mg/dL for fasting and below 120 mg/dL after meals․ This data is crucial for adjusting diet, exercise, and medication to maintain optimal health during pregnancy․
2․3 Including Insulin Doses and Medications
Recording insulin doses and medications in a gestational diabetes log sheet is crucial for managing blood sugar levels effectively․ This section helps track the type, dosage, and timing of insulin or oral medications, ensuring consistency and adherence to treatment plans․ By documenting these details, women can monitor how medications impact their blood glucose levels and make necessary adjustments in consultation with their healthcare providers to maintain optimal control and minimize complications․
Managing Gestational Diabetes
Managing gestational diabetes involves lifestyle changes and medical interventions to maintain healthy blood sugar levels․ It includes tracking blood sugar, adjusting diet, increasing physical activity, and using medications when necessary․ Regular monitoring ensures a healthy pregnancy and reduces complications․
3․1 Dietary Recommendations
Dietary recommendations for managing gestational diabetes focus on balanced meals to control blood sugar levels․ Emphasize whole, unprocessed foods like vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains․ Monitor carbohydrate intake to avoid spikes in blood glucose․ Avoid sugary drinks and refined carbohydrates․ Incorporate healthy fats and fiber-rich foods to promote satiety and stabilize blood sugar․ Portion control and meal timing are crucial to maintain optimal glucose levels throughout the day․
3․2 Exercise and Physical Activity
Regular physical activity helps manage blood sugar levels and improves overall health in gestational diabetes․ Activities like walking, swimming, and prenatal yoga are recommended․ Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise most days of the week․ Consult your healthcare provider to create a safe exercise plan tailored to your pregnancy and health status․ Consistency in physical activity supports better glucose control and reduces pregnancy complications․
3․3 Role of Medication
Medication plays a crucial role in managing gestational diabetes when lifestyle changes alone are insufficient․ Insulin is the most commonly prescribed medication, as it safely controls blood sugar levels without harming the fetus․ Oral medications may be considered in some cases, but insulin remains the preferred treatment․ Regular blood sugar monitoring and dose adjustments are essential to maintain target levels․ Always follow your healthcare provider’s guidance to ensure safe and effective management of gestational diabetes․

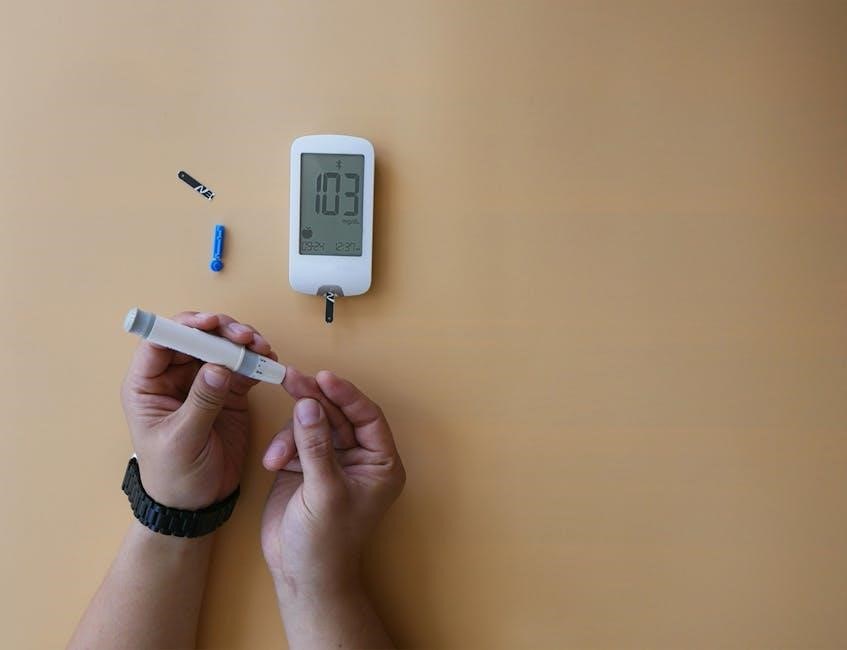
Tracking and Monitoring
Tracking and monitoring blood sugar levels is crucial for managing gestational diabetes․ Regular logging of fasting, postprandial levels, and insulin doses helps maintain control and improve outcomes․

4․1 How to Use a Weekly Log Sheet
A weekly log sheet helps track blood sugar levels, insulin doses, and meals․ Record fasting levels in the morning and after each meal․ Note physical activity and any symptoms․ Bring the completed log to doctor visits for personalized advice․ This tool ensures consistent monitoring and helps identify patterns, making it easier to manage gestational diabetes effectively and maintain healthy blood sugar levels throughout pregnancy․
4․2 Understanding Blood Sugar Target Levels
Blood sugar target levels are crucial for managing gestational diabetes․ Typically, fasting levels should be below 90 mg/dL, and postprandial levels below 120 mg/dL․ These targets help prevent complications for both mother and baby․ Regular monitoring ensures levels stay within a healthy range, maintaining pregnancy safety and reducing risks․ Adhering to these targets promotes better health outcomes and supports overall diabetes management during pregnancy․
4․3 Interpreting Log Data for Better Management
Interpreting log data helps identify patterns and trends in blood sugar levels, enabling adjustments to diet, exercise, or medication․ By analyzing fasting and postprandial readings, women can pinpoint triggers and optimize their management strategies․ Regular review of log sheets allows healthcare providers to assess progress and make informed decisions, ensuring better control of gestational diabetes and improving pregnancy outcomes while minimizing complications․

Complications and Risks
Gestational diabetes can lead to complications like preeclampsia, cesarean delivery, and fetal macrosomia if uncontrolled․ It also increases the risk of type 2 diabetes for both mother and baby․
5․1 Impact of Uncontrolled Blood Sugar on Mother and Baby
Uncontrolled blood sugar in gestational diabetes increases risks for both mother and baby․ Mothers may develop preeclampsia or require cesarean delivery, while babies face macrosomia, birth injuries, and hypoglycemia․ Persistent high glucose levels can also lead to stillbirth and respiratory distress in newborns․ Additionally, uncontrolled blood sugar raises the likelihood of complications like hypertension and premature labor, affecting long-term health outcomes for both mother and child, including future diabetes risks for the baby․
5․2 Long-Term Health Risks
Women with gestational diabetes face increased long-term risks of developing type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular diseases․ Uncontrolled blood sugar during pregnancy can also lead to metabolic syndrome and hypertension․ Babies exposed to high glucose levels in utero may experience insulin resistance and obesity later in life, elevating their risk of diabetes and heart conditions․ Managing blood sugar during pregnancy is crucial to reduce these long-term health complications for both mother and child․

Lifestyle Changes and Support
Lifestyle changes are crucial for managing gestational diabetes․ Personalized meal plans and regular physical activity promote healthy blood sugar levels, while emotional support ensures overall well-being and positive outcomes․
6․1 Creating a Personalized Meal Plan
A personalized meal plan is tailored to manage blood sugar levels, ensuring balanced nutrition for both mother and baby․ It focuses on portion control, healthy carbohydrates, proteins, and fats․ Consulting a dietitian helps create a structured plan, promoting stable glucose levels and weight management․ Regular updates based on blood sugar logs ensure the plan adapts to changing needs, fostering a healthy pregnancy outcome and reducing complications․
6․2 Staying Active During Pregnancy
Regular physical activity helps manage blood sugar levels and supports a healthy pregnancy․ Safe exercises like walking, swimming, or prenatal yoga can improve insulin sensitivity and overall well-being․ It’s important to consult a healthcare provider before starting any new routine․ Moderate activity, 30 minutes most days, is often recommended․ Tracking physical activity in a gestational diabetes log sheet can help maintain consistency and monitor its impact on blood sugar levels effectively․
6․3 Emotional Support and Counseling
Emotional support and counseling play a vital role in managing gestational diabetes․ Stress and anxiety can impact blood sugar levels, making mental health care essential․ Joining support groups or seeking professional counseling can provide coping strategies and reduce feelings of isolation․ Sharing experiences with others facing similar challenges fosters a sense of community and encouragement․ Additionally, counseling can address concerns about pregnancy and long-term health, ensuring a holistic approach to managing the condition effectively․

Postpartum Care and Follow-Up
Postpartum care involves monitoring for lingering glucose issues and preventing future diabetes․ Regular screenings and check-ups ensure early detection of potential health concerns, promoting long-term well-being․
7․1 Screenings After Pregnancy
Postpartum screenings are crucial for women with gestational diabetes to monitor blood glucose levels and detect any lingering issues․ These screenings typically include blood glucose tests and a 75g oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) 4-12 weeks after delivery․ This helps identify individuals at risk of developing type 2 diabetes and ensures timely intervention․ Regular check-ups with healthcare providers are essential for maintaining long-term health and preventing future complications․
These screenings also provide an opportunity to discuss lifestyle changes and preventive measures, ensuring a smooth transition to a personalized health plan․
7․2 Preventing Future Diabetes
Preventing future diabetes involves adopting a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet, regular physical activity, and weight management․ Women with a history of gestational diabetes should engage in moderate exercise, such as walking, and maintain a healthy weight to reduce the risk of developing type 2 diabetes․ Regular health check-ups and education on recognizing early symptoms of diabetes are also key to long-term prevention and maintaining overall well-being․

Resources and Tools
Gestational diabetes log sheets are available as free PDF downloads, offering structured templates to track blood sugar levels, meals, and medications․ Mobile apps and online communities provide additional support for managing the condition effectively․
8․1 Free Downloadable Log Sheets
Free downloadable log sheets for gestational diabetes are widely available online, offering customizable templates to track blood sugar levels, insulin doses, and meal plans․ Websites like GD UK provide PDF formats that can be printed or digitally filled out, helping women monitor their condition effectively․ These sheets often include sections for fasting and postprandial readings, medication schedules, and notes for healthcare providers, ensuring comprehensive management of gestational diabetes․
8․2 Mobile Apps for Tracking
Mobile apps like MyNetDiary and Glucose Buddy offer convenient tools for tracking gestational diabetes․ These apps allow users to log blood sugar levels, carbohydrate intake, and insulin doses in real-time․ Many apps sync with blood glucose meters, providing seamless data entry and detailed reports․ They also offer reminders for testing and medication, as well as nutritional advice․ Such apps empower women to manage their condition effectively and share data with healthcare providers for better pregnancy outcomes․
8․3 Online Communities and Forums
Online communities and forums provide valuable support for women managing gestational diabetes․ Platforms like Diabetes UK and specialized pregnancy groups offer spaces to share experiences, ask questions, and gain insights from others․ These forums often include discussions on log sheet usage, meal planning, and emotional support․ They also provide access to educational resources and expert advice, fostering a sense of connection and empowerment for those navigating gestational diabetes during pregnancy․

